863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
PatrickSUDO 2021-02-08 LeetCode-MediumBFSDFS
LeetCode 863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
# Problem:
We are given a binary tree (with root node root), a target node, and an integer value K.
Return a list of the values of all nodes that have a distance K from the target node. The answer can be returned in any order.
# Example 1:
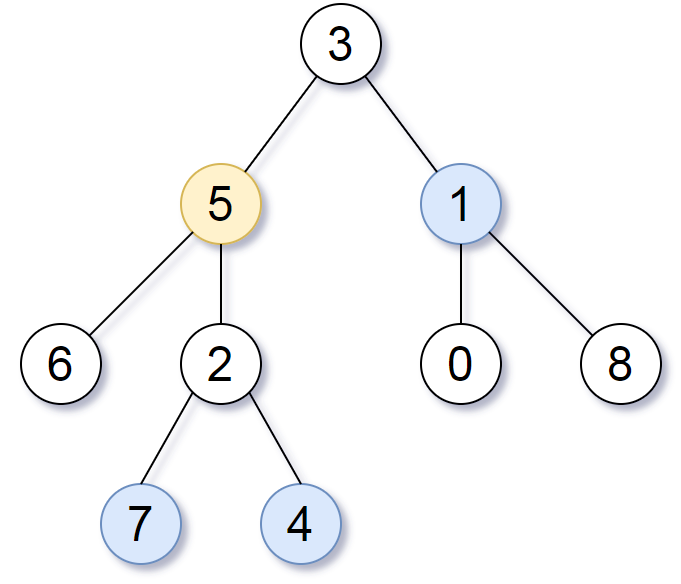
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation:
The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5)
have values 7, 4, and 1.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
# Note:
- The given tree is non-empty.
- Each node in the tree has unique values 0 <= node.val <= 500.
- The target node is a node in the tree.
- 0 <= K <= 1000.
# Solution:
In the form of the binary tree, it's not that convenient to calculate the distance from the target to any other nodes. Here, we convert the tree to the graph using the hash map. We can then use BFS to iterate through the graph starting from the target layer by layer. We use the queue to perform BFS. When the step is equal to K, we add this node's value to the ans.
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
# Python
from collections import defaultdict, deque
class Solution:
def distanceK(self, root: TreeNode, target: TreeNode, K: int) -> List[int]:
graph = defaultdict(list)
def dfs(parent, child):
if parent and child:
graph[parent.val].append(child.val)
graph[child.val].append(parent.val)
if child.left: dfs(child, child.left)
if child.right: dfs(child, child.right)
dfs(None, root)
q = deque()
q.append(target.val)
visited = set([target.val])
ans = []
d = 0
while q and d <= K:
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
node = q.popleft()
if d == K:
ans.append(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
q.append(neighbor)
visited.add(neighbor)
d += 1
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# Java
class Solution {
Map<TreeNode, List<TreeNode>> graph = new HashMap<>();
public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) {
dfs(root, null);
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<TreeNode> visited = new HashSet<>();
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int step = 0;
q.add(target);
while(!q.isEmpty() && step <= K){
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size ; i ++){
TreeNode curr = q.poll();
visited.add(curr);
if(step == K) ans.add(curr.val);
for(TreeNode nxt: graph.getOrDefault(curr, new ArrayList<TreeNode>())){
if(visited.contains(nxt)) continue;
q.add(nxt);
}
}
step++;
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode parent){
if(root != null && parent != null){
graph.putIfAbsent(root, new ArrayList<TreeNode>());
graph.putIfAbsent(parent, new ArrayList<TreeNode>());
graph.get(root).add(parent);
graph.get(parent).add(root);
}
if(root.left != null) dfs(root.left, root);
if(root.right != null) dfs(root.right, root);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39